Abstract
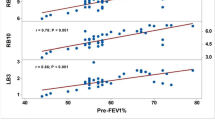
To investigate the relationship between the emphysematous changes and bronchodilator responses in patients with chronic airflow obstruction (CAO), we studied the correlation between bronchodilator response to 10 mg inhaled metaproterenol and the extent of emphysema, using selective alveolobronchogram (SAB). Fifty-one patients with CAO were classified into 3 groups by the extent of emphysematous changes detected by SAB. In group 1, no or mild emphysematous change was observed on SAB (n = 9); in group 2, there were significant emphysematous changes but the involved area was less than 75% (n = 17); in group 3, emphysematous change was extensive and covered more than 75% (n = 25). The post-bronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1 sec (FEV1) of patients in group 3 was significantly lower than in groups 1 and 2. The mean value of changes of FEV1 as a percentage of predicted FEV1 of patients in group 3 was significantly lower than in groups 1 and 2. These results indicated that the extent of emphysematous change correlated positively with the severity of fixed air-flow obstruction, and negatively with the bronchodilator response.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Thoracic Society (1987) Standardization of spirometry—1987 update. Am Rev Respir Dis 136:1285–1298
Anthonisen NR, Wright EC, Hodgkin JE, and the IPPB Trial Group (1986) Prognosis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis 133:14–20
Anthonisen NR, Wright EC, and the IPPB trial group (1986) Bronchodilator response in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis 133:814–819
Aoki T, Inoue H, Sasaki H, Shimura S, Maeda S, Tomioka M et al. (1984) Relation between selective alveolo-bronchograms and pulmonary function tests in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis 129:465–472
Blair E, Hickam JB (1955) Quantitative studies of intrapulmonary gas mixing in emphysema. Am J Med 18:519
Blumenthal BJ, Greenberg SD (1972) Alveolo-bronchography: a new clinical technic in the diagnosis of emphysema. South Med J 65:905–911
Bosken CH, Wiggs BR, Pare PD, Hogg JC (1990) Small airway dimensions in smokers with obstruction to airflow. Am Rev Respir Dis 142:563–570
Cosio MG, Ghezzo H, Hogg JC, Corbin R, Loveland M, Dosman J et al. (1977) The relations between structural changes in small airways and pulmonary function tests. N Engl J Med 298:1277–1281
Eliasson O, DeGraff AC (1985) Criteria for reversibility and obstruction in bronchodilator trials. Am Rev Respir Dis 132:858–864
Goddard PR, Nicholson EM, Laszlo G, Watt I (1982) Computed tomography in pulmonary emphysema. Clin Radiol 33:379–387
Gould GA, Macnee W, McLean A, Warren PM, Redpath A, Best JJK et al. (1988) CT measurement of lung density in life can quantitate distal airspace enlargement—an essential defining feature of human emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis 137:380–392
Hale KA, Ewing SL, Gonsnell BA, Niewoehner DE (1984) Lung disease in long-term cigarette smokers with and without chronic air-flow obstruction. Am Rev Respir Dis 130:716–721
Mitchell RS, Stanford RE, Johnson JM, Silvers GW, Dart G, George MS (1976) The morphologic features of the bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli in chronic airflow obstruction: a clinicopathologic study. Am Rev Respir Dis 144:137–145
Morrison NJ, Abboud RT, Ramadan F, Miller RR, Gibson NN, Ebans KG et al. (1989) Comparison of single breath carbon monoxide diffusing capacity and pressure-volume curves in detecting emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis 139:1179–1187
Musk AW, Gandevia B, Plamer FJ (1978) Peripheral pooling of bronchographic contrast material: evidence of its relationship to smoking and emphysema. Thorax 33: 193–200
Nagai A, West WW, Thurlbeck WM (1985) The national institutes of health intermittent positive-pressure breathing trial: pathology studies. II. Correlation between morphologic findings, clinical findings, and evidence of expiratory air-flow obstruction. Am Rev Respir Dis 132:946–953
Nakamura T, Takizawa T, Takishima T, Konno K (1969) Selective alveolo-bronchography in chronic pulmonary emphysema. Tohoku J Exp Med 99:207–223
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Division of Lung Diseases Workshop Report (1985) The definition of emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis 132:182–185
Postma DS, De Vries K, Kocter GH, Sluiter HJ (1986) Independent influences of reversibility of air-flow obstruction and nonspecific hyperreactivity on the long-term course of lung function in chronic air-flow obstruction. Am Rev Respir Dis 134:276–280
Sargent EN, Sherwin R (1971) Selective wedge bronchography. Am J Roentgenol 113:660–679
Sasaki H, Okayama H, Aikawa T, Shimura S, Sekizawa K, Yanai M et al. (1986) Central and peripheral airways as determinants of ventilatory function in patients with chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and bronchial asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis 134:1182–1189
Symonds G, Renzetti, Jr. AD, Mitchell MM (1974) The diffusing capacity in pulmonary emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis 109:391–394
Tanaka M, Satoh M, Kawanami O, Aihara K (1985) A new bronchofiberscope for the study of diseases of very peripheral airways. Chest 85:590–594
Wright JL, Lawson LM, Pare PD, Wiggs BJ, Kennedy D, Hogg JC (1983) Morphology of peripheral airways in current smokers and ex-smokers. Am Rev Respir Dis 127:474–477
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: H. Koyama
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koyama, H., Nishimura, K., Mio, T. et al. Emphysematous changes assessed by selective alveolobronchography and bronchodilator response in chronic airflow obstruction. Lung 172, 103–112 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00185081
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00185081