Summary
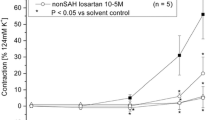
We examined the effects of the recently developed calcium antagonist HA1077 on cerebral haemodynamics during the chronic stage of the two-haemorrhage canine model system of vasospasm. Regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF), regional cerebral blood velocity and regional cerebral blood volume in the canine parietal cortex were measured by Laser-doppler flowmeter. On the 7th day after the initial injection of autogenous blood, subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) produced a significant decrease in rCBF (59% of control, p<0.05) and Hood velocity (48% of control, p<0.05), with no remarkable change in blood volume (108% of control). Bolus intravenous administration of HA1077 (0.1–0.3 mg/kg) dose-dependently increased the rCBF and blood velocity, without significantly changing the blood volume on Day 7 after SAH. HA1077 improves haemodynamic function manifested by an increase in rCBF and velocity in this SAH model, and may be suitable for the treatment of vasospasm in patients with SAH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn H, Lindhagen J, Nilsson GE, Öberg PÅ, Lundgren O (1986) Assessment of blood flow in the small intestine with laser doppler flowmetry. Scand J Gastroenterol 21: 863–870
Asano T, Ikegaki I, Satoh S, Suzuki Y, Shibuya M, Takayasu M, Hidaka H (1987) Mechanism of action of a novel antivasospasm drug, HA1077. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 241: 1033–1040
Asano T, Suzuki T, Tsuchiya M, Satoh S, Ikegaki I, Shibuya M, Suzuki Y, Hidaka H (1989) Vasodilator actions of HA1077 in vitro and in vivo putatively mediated by the inhibition of protein kinase. Br J Pharmacol 98: 1091–1100
Chen ST, Hsu CY, Hogan EL, Maricq H, Balentine JD (1986) A model of focal ischemic stroke in the rat: Reproducible extensive cortical infarction. Stroke 17: 738–743
Diresta GR, Kiel JW, Riedel GL, Kaplan P, Shepherd AP (1987) Hybrid blood flow probe for simultaneous H2 clearance and laser-Doppler velocimetry. Am J Physiol 253: G573-G581
Gibbs JM, Wise RJS, Leenders KL, Jones T (1984) Evaluation of cerebral perfusion reserve in patients with carotid-artery occlusion. The Lancet i: 310–314
Grubb RL Jr, Raichle ME, Eichung JO, Gado MH (1977) Effects of subarachnoid hemorrhage on cerebral blood volume, blood flow, and oxygen utilization in humans. J Neurosurg 46: 446–453
Haberl RL, Heizer ML, Marmarou A, Ellis EF (1989) Laser-Doppler assessment of brain microcirculation: effect of systemic alterations. Am J Physiol 256: H1247-H1254
Jan M, Buchheit F, Tremoulet M (1988) Therapeutic trial of intravenous nimodipine in patients with established cerebral vasospasm after rupture of intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 23: 154–157
Lindsberg RJ, O'Neill JT, Paakkari IA, Hallenbeck JM, Feuerstein G (1989) Validation of laser-Doppler flowmetry in measurement of spinal cord blood flow. Am J Physiol 257: H674–680
Mee E, Dorrance D, Lowe D, Neil-Dwyer G (1988) Controlled study of nimodipine in aneurysm patients treated early after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 22: 484–491
Petruk KC, West M, Mohr G,et al (1988) Nimodipine treatment in poor-grade aneurysm patients. J Neurosurg 68: 505–517
Pickard JD, Murray GD, Illingworth R,et al (1989) Effect of oral nimodipine on cerebral infarction and outcome after subarachnoid haemorrhage: British aneurysm nimodipine trial. Br Med J 298: 636–642
Powers WJ, Grubb RL Jr, Baker RP, Mintun MA, Raichle ME (1985) Regional cerebral blood flow and metabolism in reversible ischemia due to vasospasm. J Neurosurg 62: 539–546
Rosenblum BR, Bonner RF, Oldfield EH (1987) Intraoperative measurement of cortical blood flow adjacent to cerebral AVM using laser Doppler velocimetry. J Neurosurg 66: 396–399
Rundquist I, Smith QR, Michel ME, Ask P, Öberg PÅ, Rapoport SI (1985) Sciatic nerve blood flow measured by laser Doppler flowmetry and [14C] iodoantipyrine. Am J Physiol 248: H311-H317
Sasaki Y, Sasaki Y, Kanno K, Hidaka H (1987) Disorganization of calcium antagonists of actin microfilament in aortic smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol 253: C71-C78
Shibuya M, Suzuki Y, Takayasu M, Asano T, Harada T, Ikegaki I, Satoh S, Hidaka H (1988) The effects of an intracellular calcium antagonist HA1077 on delayed cerebral vasospasm in dogs. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 90: 53–59
Spelman FA, Öberg PÅ, Astley C (1986) Localized neural control of blood flow in the renal cortex of the anaesthetized baboon. Acta Physiol Scand 127: 437–441
Suzuki Y, Shibuya M, Takayasu M, Asano T, Ikegaki I, Satoh S, Saito M, Hidaka H (1988) Protein kinase activity in canine basilar arteries after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 22: 1028–1031
Takayasu M, Suzuki Y, Shibuya M, Asano T, Kanamori M, Okada T, Kageyama N, Hidaka H (1986) The effects of HA compound calcium antagonists on delayed cerebral vasospasm in dogs. J Neurosurg 65: 80–85
Varsos VG, Liszczak TM, Han DH, Kistler JP, Vielma J, Black PM, Heros RC, Zervas NT (1983) Delayed cerebral vasospasm is not reversible by aminophylline, nifedipine, or papaverine in a “two-hemorrhage” canine model. J Neurosurg 58: 11–17
Yamakami I, Isobe K, Yamaura A, Nakamura T, Makino H (1983) Vasospasm and regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) in patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysm: Serial rCBF studies with the Xenon-133 inhalation method. Neurosurgery 13: 394–401
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Satoh, S., Suzuki, Y., Ikegaki, I. et al. The effects of HA1077 on the cerebral circulation after subarachnoid haemorrhage in dogs. Acta neurochir 110, 185–188 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01400689
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01400689