Summary
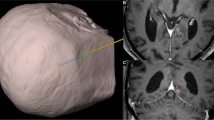
On the base of a stereotactic device originally described by Riechert and Mundinger a three-dimensional localization and treatment planning system for CT-guided computer assisted stereotactic procedures has been developed. The experience with 338 patients, in which image guided stereotaxy has been used for the assessment of various intracerebral lesions, is presented. In 54 of these patients the cannula was introduced with a 20 MHz Doppler-probe positioned at the tip of the needle. A comparison of tissue specimens taken stereotactically with tissue material after tumour resection and/or autopsy was performed in 35 patients. The accuracy of the histological diagnosis was 88%. Bleeding as a complication due to the stereotactic intervention occurred in 8 patients (2.4%). Two of these patients had a fatal outcome (mortality: 0.6%). The morbidity (transient and permanent deterioration of the clinical status) was 1.2%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apuzzo MLJ, Chandrasoma PT, Cohen D, Zee CS, Zelman V (1987) Computed imaging stereotaxy: experience and perspective related to 500 procedures applied to brain masses. Neurosurgery 20: 931–937
Backlund E-O (1971) A new instrument for stereotaxic brain tumour biopsy (technical note). Acta Chir Scand 137: 825–827
Blaauw G, Braakman R (1988) Pitfalls in diagnostic brain surgery. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Suppl] 42: 161–165
Boethius J, Bergstrom M, Greitz T (1980) Stereotactic computerized tomography with a Ge 8800 scanner. J Neurosurg 52: 794–800
Brown RA (1979) A computerized tomography-computer graphics approach to stereotaxic localization. J Neurosurg 50: 715–720
Chandrasoma PT, Smith MM, Apuzzo MLJ (1989) Stereotactic biopsy in the diagnosis of brain masses: comparison of results of biopsy and resected surgical specimen. Neurosurgery 24: 160–165
Colombo F, Casentini L, Zanusso M, Danieli D, Benedetti A (1988) Validity of stereotactic biopsy as a diagnostic tool. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Suppl] 42: 152–156
Edner G (1984) Stereotactic biopsy of intracranial space occupying lesions. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 57: 213–234
Feiden W, Steude U, Bise K, Gündisch O (1991) Accuracy of stereotactic brain tumour biopsy: comparison of the histologic findings in biopsy cylinders and resected tumour tissue. Neurosurg Rev 14: 51–56
Feiden W, Bise K, Steude U (1990) Diagnosis of primary cerebral lymphoma with particular reference to CT-guided stereotactic biopsy. Virchows Archiv (A) 417: 21–28
Gahbauer H, Sturm V, Schlegel W, Pastyr O, Scharfenberg H, Zable HJ, van Kaick G, Netzeband G, Scheer KE, Schabbert S (1983) Combined use of stereotaxic CT and angiography for brain biopsies and stereotaxic irradiation. AJNR 4: 715–718
Gilsbach J (1983) Intra-operative Doppler sonography in neurosurgery. Springer, Wien New York
Gilsbach J, Mohadjer M, Mundinger F (1987) A new safety device to prevent bleeding complications during stereotactic biopsy-the “stereotactic” Doppler sonography. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 89: 77–79
Kleihues P, Volk B, Anagnostopoulos J, Kiessling M (1984) Morphologic evaluation of stereotactic brain tumour biopsies. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Suppl] 33: 171–181
Lennert K (1981) Histopathology of non-Hodgkin's lymphomas (based on the Kiel classification). Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Leksell I, Jernberg B (1980) Stereotaxis and tomography. A technical note. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 52: 1–7
Monsaingeon V, Daumas-Duport C, Mann M, Miyahara S, Szikla G (1984) Stereotactic sampling biopsies in a series of (268) consecutive cases — validity and technical aspects. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Suppl] 33: 195–200
Munari C, Rosler Jr J, Musolino A, Betti OO, Daumas-Duport C, Missir O, Chodkiewicz JP (1989) Differential diagnosis between tumoural and non-tumoural intracranial lesions in children: a stereotactic approach. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Suppl] 46: 75–78
Mundinger F, Birg W, Klar M (1978) Computer assisted stereotactic brain operations by means including computerized axial tomography. Appl Neurophysiol 41: 169–182
Mundinger F (1982) CT-stereotactic biopsy of brain tumours. In: Voth D, Gutjahr P, Langmaid C (eds) Tumours of the central nervous system in infancy and childhood. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 234–246
Mundinger F, Birg W (1984) Stereotactic biopsy of intracranial processes. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Suppl] 33: 219–224
Mundinger F (1985) CT-stereotactic biopsy for optimizing the therapy of intracranial processes. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Suppl] 35: 70–74
Ostertag CB, Mennel HD, Kiessling M (1980) Stereotactic biopsy of brain tumours. Surg Neurol 14: 275–283
Riechert T, Mundinger F (1955) Beschreibung und Anwendung eines Zielgerätes für stereotaktische Hirnoperationen. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Suppl] 3: 308–337
Scerrati M, Rossi GF (1984) The reliability of stereotactic biopsy. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Suppl] 33: 201–205
Schlegel WJ, Scharfenberg H, Sturm V, Penzholz H, Lorenz WJ (1981) Direct visualization of intracranial tumours in stereotactic and angiographic films by computer calculation of longitudinal CT-sections: a new method for stereotactic localization of tumour outlines. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 58: 27–35
Sturm V, Pastyr O, Schlegel W, Scharfenberg H, Zabel HJ, Netzeband G, Schabbert S, Berberich W (1983) Stereotactic computer tomography with a modified Riechert-Mundinger device as the basis for integrated stereotactic neuroradiological investigations. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 68: 11–17
Thomas DGT, Nouby RM (1989) Experience in 300 cases of CT-directed stereotactic surgery for lesion biopsy and aspiration of haematoma. Br J Neurosurg 3: 321–326
Ungersböck K, Schmidbauer M, Budka H, Kitz K, Grunert P, Koos W (1989) Stereotaktische Biopsie intrakranieller Prozesse: Validität der histologischen Diagnostik. Wien Klin Wochenschr 101: 376–380
Valk PE, Budinger TF, Levin VA, Silver P, Gutin PH, Doyle WK (1988) PET of malignant cerebral tumours after interstitial brachytherapy. Demonstration of metabolic activity and correlation with clinical outcome. J Neurosurg 69: 830–838
Wise BL, Gleason C (1979) CT directed stereotactic surgery for diagnosis and treatment of deep cerebral lesions. Annual Meeting of AANS, Los Angeles, California
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Voges, J., Schröder, R., Treuer, H. et al. CT-guided and computer assisted stereotactic biopsy. Acta neurochir 125, 142–149 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01401842
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01401842