Summary
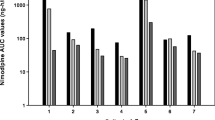
Measurement of plasma alpha-humanANP (ANP) and antidiuretic hormone (ADH) in 28 cases with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) was carried out, and then compared with control subjects who were infused with hypertonic saline.
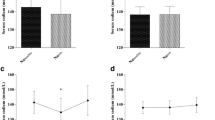
In cases with hyponatremia (HN), statistical correlation between control subjects and cases without HN was not evident with regards to ANP and plasma osmolality (Posm), excreted fraction of filtrated sodium (FENa) and urinary Na/K. Furthermore, they secreted supernumerarilly in spite of HN.
Cases with HN were further subdivided into two groups, they were those cases with negative total sodium balance at the time of appearance of HN, and those cases without total negative sodium balance. In the former, central venous pressure had a tendency to decrease, however, secretion of ANP and ADH was statistically not different in either groups.
It appears that ANP regulated urinary sodium excretion against an osmotic or sodium load acts as a maintenance of homeostasis as an osmotic regulator. Cases with HN in which secretion of ADH was physiological, ANP secreted supernumerarilly in spite of hypoosmonaemia and hypovolaemia.
Our findings may contribute to a better understanding of the pathophysiological processes leading to hyponatremia in cases with cerebral disorders, and may help to improve the treatment possibilities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballermann BJ, Brenner BM (1986) Role of atrial peptides in body fluid homeostasis. Circ Res 58: 619–630
Dunn FL, Brennan YJ, Nelson AE, Rovertson GL (1973) The role of blood osmolality and volume in regulating vasopressin in the rat. J Clin Invest 52: 3212–3219
Gruber KA, Whitaker JM, Vardman MB Jr (1980) Endogenous digitalis-like substance in plasma of volume-expanded dogs. Nature 287: 743–745
Itoh H, Nakao K, Morii N, Yamada T, Shiono S, Sakamoto M, Sugawara A, Saito Y, Katsuura G, Shiomi T, Eigyo M, Matsushita A, Imura H (1986) Central action of atrial natriuretic polypeptide on blood pressure in conscious rat. Brain Res Bull 16: 745–749
Itoh H, Nakao K, Katsuura G, Morii N, Shiono S, Sakamoto M, Sugawara A, Yamada T, Saito Y, Matsushita A, Imura H (1987) Centrally infused atrial natriuretic polypeptide attenuates exaggerated salt appetite in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Circ Res 59: 342–347
Itoh H, Nakao K, Katsuura G, Morii N, Yamada T, Shiono S, Sakamoto M, Sugawara A, Saito W, Eigyo M, Matsushita A, Imura H (1986) Possible involvement of central atrial natriuretic polypeptide in regulation of hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis in conscious rat. Neurosci Lett 69: 254–258
Kamoi K, Sato F, Aral O, Miyuki I, Yamaji T (1986) Plasma atrial natriuretic polypeptide (ANP) as a third factor in patients with hyponatremia. Igaku no Ayumi (Tokyo) 138: 111–112
Kangawa K, Matsuo H (1984) Purification and complete amino acid sequence of alpha-human atrial natriuretic polypeptide (alpha-hANP). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 118: 131–139
Morii N, Nakao K, Sugawara A, Sakamoto M, Suda M, Shimokura M, Kiso Y, Kihara M, Yamori Y, Imura H (1985) Occurrence of atrial natriuretic polypeptide in brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 127: 413–419
Nakamura M, Katsuura G, Nakao K, Imura H (1985) Antidipsogenic action of alpha-human atrial natriuretic polypeptide administrated intracerebroventricularly in rats. Neurosci Lett 58: 1–6
Nelson PB, Seif SM, Maroon JC, Robinson AG (1981) Hyponatremia in intracranial disease: perhaps not the syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH). J Neurosurg 55: 938–941
Peters JP, Welt LG, Sims EAH, Orloff J, Needham JW (1950) A salt wasting syndrome associated with cerebral disease. Trans Assoc Am Physicians 63: 57–64
Rovertson GL, Athar S (1976) The interaction of blood osmolality and blood volume in regulating plasma vasopressin in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 42: 613–620
Schwartz WB, Bennet W, Curelop S, Bartter FC (1957) A syndrome of renal sodium loss and hyponatremia, probably from inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone. Am J Med 23: 529–542
Segar WE, Moore WW (1968) The regulation of antidiuretic hormone in man. I. Effects of change in position and ambient temperature on blood ADH levels. J Clin Invest 47: 2143–2151
Sugawara A, Nakao K, Morii N, Sakamoto M, Suda M, Shimokura M, Kiso Y, Kihara M, Yamori Y, Nishimura K, Soneda J, Ban T, Imura H (1985) Alpha-human natriuretic polypeptide is released from the heart and circulates in the body. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 129: 439–446
Welt LG, Seldin DW, Nelson WP, German WJ, Peters JP (1952) Role of the central nervous system in metabolism of electrolytes and water. Arch Int Med 90: 355–378
Wijdicks EF, Vermeulen M, ten Haaf JA, Hijdra A, Bakker WH, van Gijn J (1985) Volume depletion and natriuresis in patients with a ruptured intracranial aneurysm. Ann Neurol 18: 211–216
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimoda, M., Yamada, S., Yamamoto, I. et al. Atrial natriuretic polypeptide in patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage due to aneurysmal rupture. Acta neurochir 97, 53–61 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01577740
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01577740