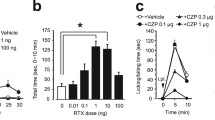
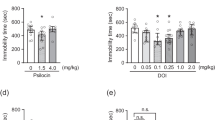
Summary
Acute (1h) intraperitoneal (ip) treatment with interferon (IFN)-α-2a (300IU/g) significantly inhibited wet-dog shakes (WDS) induced by (±)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2 aminopropane (DOI; 0.5, 1.0mg/kg), which is mediated by serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT)2 receptor in rats. IFN-α did not affect spontaneous locomotion. The inhibition of DOI (0.5mg/kg)-induced WDS by IFN-α was dose (90–300 IU/g)- and time (1–6 h)-dependent, and was prevented by 30 min pretreatment with naltrexone (NLTX; 1.0mg/kg, ip), an opioid receptor antagonist. Acute (1h) intracerebroventricular (icv) treatment with IFN-α (1,500IU/rat) also inhibited DOI (0.5mg/kg)-induced WDS, and the effect was blocked by NLTX (50μg/rat, icv). These results suggest that IFN-α may modulate 5-HT2 receptor-mediated behavior through opioid receptors in the central nervous system.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CNS :
-
central nervous system
- DOI :
-
(±)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2 aminopropane
- 5-HT :
-
5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin)
- icv :
-
intracerebroventricular
- IFN :
-
interferon
- ip :
-
intraperitoneal
- IU :
-
international unit
- NLTX :
-
naltrexone
- sc :
-
subcutaneous
- WDS :
-
wet-dog shakes
References
Adams F, Fernandez F, Mavligit G (1988) Interferon-induced organic mental disorders associated with unsuspected pre-existing neurologic abnormalities. J Neuro-Oncol 6: 355–359
Birmanns B, Saphier D, Abramsky O (1990) α-Interferon modifies cortical EEG activity: dose-dependence and antagonism by naloxone. J Neurol Sci 100: 22–26
Blalock JE, Smith EM (1980) Human leukocyte interferon: structural and biological relatedness to adrenocorticotropic hormone and endorphins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77: 5972–5974
Blalock JE, Smith EM (1981) Human leukocyte interferon (huIFN-α): potent endorphinlike opioid activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 101: 472–478
Crnic LS, Segall MA (1992a) Prostaglandins do not mediate interferon-α effects on mouse behavior. Physiol Behav 51: 349–352
Crnic LS, Segall MA (1992b) Behavioral effects of mouse interferons-α and -γ and human interferon-α in mice. Brain Res 590: 277–284
Dunn AL, Crnic LS (1993) Repeated injections of interferon-α A/D in Balb/c mice: behavioral effects. Brain Behav Immun 7: 104–111
Dursun SM, Handley SL (1993) The effects of α2-adrenoceptor antagonists on the inhibition of 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane (DOI)-induced head shakes by 5-HT1A receptor agonists in the mouse. Br J Pharmacol 109: 1046–1052
Fone KCF, Robinson AJ, Marsden CA (1991) Characterization of the 5-HT receptor subtypes involved in the motor behaviours produced by intrathecal administration of 5-HT agonists in rats. Br J Pharmacol 103: 1547–1555
Garssadi SI, Mandi Y, Regely K, Tarodi B, Beladi I (1993) The inhibitory effect of interferon-alpha on the serotonin-induced impairment of human NK cell activity in whole blood. Brain Behav Immun 7: 164–175
Gisslinger H, Svoboda T, Clodi M, Gilly B, Ludwig H, Havelec L, Luger A (1993) Interferon-α stimulates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in vivo and in vitro. Neuroendocrinology 57: 489–495
Green AR, O'Shaughnessy K, Hammond M, Schachter M, Grahame-Smith DG (1983) Inhibition of 5-hydroxytryptamine-mediated behavior by the putative 5-HT2 antagonist pirenperone. Neuropharmacology 22: 573–578
Gutterman JU, Fine S, Quesada J, Horning SJ, Levine JF, Alexanian R, Bernhardt L, Kramer J, Spiegel H, Colburn W, Trown P, Merigan T, Dziewanowski Z (1982) Recombinant leukocyte α interferon: pharmacokinetics, single-dose tolerance, and biologic effects in cancer patients. Ann Intern Med 96: 549–556
Henco K, Brosius J, Fujisawa A, Fujisawa JI, Haynes JR, Hochstadt J, Kovacic T, Pasek M, Schambock A, Schmid J, Todokoro K, Walchli M, Nagata S, Weissmann C (1985) Structural relationship of human interferon alpha genes and pseudogenes. J Mol Biol 185: 227–260
Kanai K, Iwata K, Nakao K, Kako M, Okamoto H (1990) Suppression of hepatitis C virus RNA by interferon-α. Lancet 336: 245
Kugaya A, Kagaya A, Uchitomi Y, Motohashi N, Yamawaki S (1995) Inhibition of serotonin-induced Ca2+ mobilization by interleukin-1β in rat C6BU-1 glioma cells. Brain Res 682: 151–156
Kuroda Y, Mikuni M, Ogawa T, Takahashi K (1992) Effect of ACTH, adrenalectomy and the combination treatment on the density of 5-HT2 receptor binding sites in neocortex of rat forebrain and 5-HT2 receptor-mediated wet-dog shake behaviors. Psychopharmacology 108: 27–32
Kusumi I, Koyama T, Yamashita I (1991) Serotonin-stimulated Ca2+ response is increased in blood platelets of depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry 30: 310–312
Lee PHK, Obie J, Hong J-S (1989) Opioids induce convulsions and wet dog shakes in rats: mediation by hippocampal mu, but not delta or kappa opioid receptors. J Neurosci 9: 692–697
Mannering GJ, Deloria LB (1986) The pharmacology and toxicology of the interferons: an overview. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 26: 455–515
McDonald EM, Mann AH, Thomas HC (1987) Interferons as mediators of psychiatric morbidity. Lancet ii: 1175–1178
Meyers CA, Scheibel RS, Forman AD (1991) Persistent neurotoxicity of systemically administered interferon-alpha. Neurology 41: 672–676
Mikuni M, Kusumi I, Kagaya A, Kuroda Y, Mori H, Takahashi K (1991) Increased 5-HT2 receptor function as measured by serotonin-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis in platelets of depressed patients. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 15: 49–61
Mikuni M, Kagaya A, Takahashi K, Meltzer HY (1992) Serotonin but not norepinephrine-induced calcium mobilization of platelets is enhanced in affective disorders. Psychopharmacology 106: 311–314
Muller H, Hammes E, Hiemke C, Hess G (1991) Interferon-alpha-2-induced stimulation of ACTH and cortisol secretion in man. Neuroendocrinology 54: 499–503
Nakashima T, Hori T, Kuriyama K, Matsuda T (1988) Effects of interferon-α on the activity of preoptic thermosensitive neurons in tissue slices. Brain Res 454: 361–367
Okamoto Y, Kagaya A, Shinno H, Motohashi N, Yamawaki S (1995) Serotonin-induced platelet calcium mobilization is enhanced in mania. Life Sci 56: 327–332
Pranzatelli MR (1990) Evidence for involvement of 5-HT2 and 5-HT1C receptors in the behavioral effects of the 5-HT agonist 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl aminopropane)-2 (DOI). Neurosci Lett 115: 74–80
Renault PF, Hoofnagle JH, Park Y, Mullen KD, Peters M, Jones DB, Rustgi V, Jones EA (1987) Psychiatric complications of long-term interferon alfa therapy. Arch Intern Med 147: 1577–1580
Roosth J, Pollard RB, Brown SL, Meyer WJ (1986) Cortisol stimulation by recombinant interferon-α2. J Neuroimmunol 12: 311–316
Schnittman SM, Vogel S, Baseler M, Lane HC, Davey RT Jr (1994) A phase I study of interferon-α2b in combination with interleukin-2 in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Infect Dis 169: 981–989
Segall MA, Crnic LS (1990) An animal model for the behavioral effects of Interferon. Behav Neurosci 104: 612–618
Shibata M, Blatteis CM (1991) Human recombinant tumor necrosis factor and Interferon affect the activity of neurons in the organum vasculosum laminae terminalis. Brain Res 562: 323–326
Smedley H, Katrak M, Sikora K, Wheeler T (1983) Neurological effects of recombinant human interferon. Br Med J 286: 262–264
Smith MJ, Mouawad R, Vuillemin E, Benhammouda A, Soubrane C, Khayat D (1994) Psychological side effects induced by interleukin-2/α interferon treatment. Psychooncology 3: 289–298
Take S, Mori T, Katafuchi T, Hori T (1993) Central interferon-α inhibits natural killer cytotoxicity through sympathetic innervation. Am J Physiol 265: R453-R459
Terao A, Oikawa M, Saito M (1994) Tissue-specific increase in norepinephrine turnover by central interleukin-1, but not by interleukin-6, in rats. Am J Physiol 266: R400–R404
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kugaya, A., Kagaya, A., Uchitomi, Y. et al. Effect of interferon-α on DOI-induced wet-dog shakes in rats. J. Neural Transmission 103, 947–955 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01291785
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01291785