Summary.
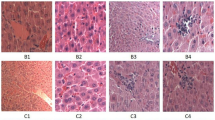
Influence of the extract of Gingko biloba (EGB-761) and one of its constituent Gingkolide B (BN-52021) on hyperthermia induced cellular damage and heat shock protein (HSP 72 kD) response was examined in a rat model. Rats subjected to 4 h heat stress at 38°C in a biological oxygen demand (BOD) incubator (relative humidity 50–55%, wind velocity 20–25 cm/sec) resulted in profound edema and cell injury in many parts of the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, cerebellum, thalamus, hypothalamus and brain stem. Immunostaining of HSP 72 kD showed marked upregulation in the damaged and distorted neurons located within the edematous area. Pretreatment with EGB-761 (50 mg/kg/day, p.o.) and BN-520 21 (2 mg/kg, p.o.) per day for 5 days significantly reduced HSP expression and attenuated cell damage. Our results show that EGB-761 and its component Gingkolide B (BN-52021) has the capacity to reduce edema and cell injury following hyperthermia and this effect of the compound is somehow associated with a reduction in cellular stress response as evidenced with a reduction in HSP expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received August 31, 1999 Accepted September 20, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Westman, J., Drieu, K. & Sharma, H. Antioxidant compounds EGB-761 and BN-520 21 attenuate heat shock protein (HSP 72 kD) response, edema and cell changes following hyperthermic brain injury . Amino Acids 19, 339–350 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007260070065
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007260070065