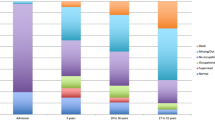
Summary
The objective of this study was to identify clinically relevant predictors of short-term (2 years) outcome in schizophrenic patients and to gather these predictors into one simple prognosis model for the course of the disease. Ninety-nine schizophrenic outpatients classified according to DSM-III criteria were observed for 3 years with regard to their relapse (rehospitalization) frequency. Predictors of both a high and a low relapse risk permitting a prognostic assessment of the individual case were based on various sources: case history data, especially those relating to the previous course of the disease; cocial and therapeutic situation; psychopathological findings; emotional family atmosphere; and prognosis scales.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atakan Z, Cliff G, Cooper JE (1990) Can psychiatrists predict the one-year outcome of schizophrenia? Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 25:117–124
Baumann U, Stieglitz RD (1983) Testmanual zum AMDP-System. In: Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Methodik und Dokumentation in der Psychiatrie (eds). Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Biehl H, Maurer K, Schubart C, Krumm B, Jung E (1986) Prediction of outcome and utilization of medical services in a prospective study of first onset schizophrenics. Eur Arch Psychiatry Neurol Sci 236:139–147
Buchkremer G, Rath N (1989) Therapeutische Arbeit mit Angehörigen schizophrener Patienten. Meßinstrumente, Methoden, Konzepte. Huber, Bern
Buchkremer G, Schulze Mönking H (1986) Die Effizienz von therapeutischen Angehörigengruppen und Selbsthilfegruppen bei der Rezidivprophylaxe schizophrener Patienten. In: Bökker W u. Brenner HD (eds) Die Bewältigung der Schizophrenie. Huber, Bern, pp 113–120
Buchkremer G, Schulze Mönking H (1987) Therapeutische Angehörigenarbeit bei rückfallgefährdeten schizophrenen Patienten. In: Heimann H, Zimmer FT (eds) Chronisch psychisch Kranke—Probleme und Stand der Behandlungs- und Forschungssituation in der Bundesrepublik Deutschland. Fischer, Stuttgart, pp 36–42
Buchkremer G, Windgassen K (1987) Leitlinien des psychotherapeutischen Umgangs mit schizophrenen Patienten-Was ist den verschiedenen Schulen und Methoden gemeinsam? Psychothen Psychosom Med Psychol 12:401–436
Buchkremer G, Schulze Mönking H, Lewandowski L, Wittgen C (1986) Emotional atmosphere in families of schizophrenic outpatients: relevance of a practice-oriented assessment instrument. In: Goldstein MJ, Hand I, Hahlweg K (eds) Treatment of schizophrenia: 79–84. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
CGI (Clinical Global Impression) (1976) In: CIPS-Collegium Internationale Psychiatriae Scalarum. Beltz, Weinheim
Ciompi L (1981) Wie können wir die Schizophrenen besser behandeln? Nervenarzt 52:506–512
Ciompi L, Müller C (1976) Lebensweg und Alter der Schizophrenen. Eine katamnestische Langzeitstudie bis ins Senium. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Derissen W (1989) Krankheitsverarbeitung und Krankheitsverlauf bei schizophrenen Psychosen. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr 57: 434–439
Endicott J, Spitzer RL, Fleiß JL, Cohen J (1976) The global assessment scale. Arch Gen Psychiatry 33:766–771
Gebhardt R, Pietzcker A, Strauss A, Stoeckel M, Langer C, Freudenthal K (1983) Skalenbildung im AMDP-System. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr 233:223–245
Glass LL, Katz HM, Schnitzer RD, Knapp PH, Frank AF, Gunderson JG (1989) Psychotherapy of schizophrenia: an empirical investigation of the relationship of process to outcome. Am J Psychiatry 146:603
Goldstein MJ (1985) Family factors that antedate the onset of schizophrenia and related disorders: the results of a fifteen year prospective longitudinal study. Acta Psychiatr Scand 71: 7–18
Heinrich K (1967) Zur Bedeutung des postremissiven Erschöpfungs-Syndroms für die Rehabilitation Schizophrener. Nervenarzt 38:487–491
Huber G, Gross G, Schüttler R (1979) Schizophrenie. Eine Verlaufs- und psychiatrische Langzeitstudie. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Jenkins JH, Karno M, Selva A, Santana F, Telles C, Lopez S, Mintz J (1986) Expressed emotion, maintenance pharmacotherapy and schizophrenic relapse among Mexican-Americans. Psychopharmacol Bull 22:621–627
Johnstone EC, Frith CD, Gold A, Stevens M (1979) The outcome of severe acute schizophrenic illness after one year. Br J Psychiatry 134:28–33
Kapfhammer HP, Rüther E (1988) Depot-Neuroleptika. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Karley YL, Gay TL, Vore M (1989) Predictors of response to high dose antipsychotics in chronic schizophrenics. Psychiatry Res 30:1–9
Knight RA, Roff JD, Barnett J, Moss JL (1979) Concurrent and predictive validity of thought disorders and affectivity: a 22-year follow up of acute schizophrenics. J Abnorm Psychol 88:1
Kreisman DE, Simmens SJ, Joy VD (1979) Rejecting the patient. Preliminary validation of a self- report scale. Schizophr Bull 5: 220–222
Martin P, Sterne AL (1976) Impairment and prediction of cognitive functioning in schizophrenics. Res Commun Psychol Psychiatry Behav 1:495
Möller HJ (1987) Indikation und Differentialindikation der neuroleptischen Langzeitmedikation. In: Pichot P, Möller HJ (eds) Neuroleptika. Tropon-Symposium II: 63–79. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Möller HJ, Zerssen D von (1985) Psychopathometrische Untersuchung zur prognostischen Bedeutung des psychopathologischen Befundes und der prämorbiden Persönlichkeit für den Entlassungszustand neuroleptisch behandelter Patienten mit schizophrenen Psychosen. Nervenarzt 56:498–505
Möller HJ, Werner-Eilert K, Wüschner-Stockheim M, Zerssen D von (1982a) Relevante Merkmale für die 5-Jahres-Prognose von Patienten mit schizophrenen und verwandten Psychosen. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr 231:305–322
Möller HJ, Zerssen D von, Werner-Eilert K, Wüschner-Stockheim M (1982b) Outcome in schizophrenic and similar paranoid psychoses. Schizophr Bull 8:99–108
Möller HJ, Scharl W, Zerssen, D von (1984) Störungen der prämorbiden sozialen Adaptation als Prädiktor für die Fünfjahresprognose schizophrener Psychosen. Nervenarzt 55:358–364
Moline RA, Singh S, Morris A, Meltzer HY (1985) Family expressed emotion and relapse in schizophrenia in 24 urban American patients. Am J Psychiatry 142:1078–1081
Nüchterlein KH, Dawson ME (1984) A heuristic vulnerabilitystress model of schizophrenic episodes. Schizophr Bull 10: 300–312
Nuechterlein KH, Snyder KS, Dawson ME, Rappe S, Gitlin M, Fogelson D (1986) Expressed emotion, fixed-dose fluphenazine decanoate maintenance and relapse in recent-onset schizophrenia. Psychopharmacol Bull 22:633–639
Parker MD, Johnston P, Hayward L (1988) Parental “expressed emotion” as a predictor of schizophrenic relapse. Arch Gen Psychiatry 45:806–811
Pichot P, Möller HJ (1987) Neuroleptika. Rückschau 1952–1986. Künftige Entwicklungen. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Pietzcker A, Gaebel W (1978) Übersetzung der Kurzform der Phillipsskala zur prämorbiden Anpassung (Harris 1975), Übersetzung der Prognose-Skala (Strauss-Carpenter 1974). Translation of version published in Schizoph Bull 3:209–212
Pietzcker A, Gaebel W (1983) Prediction of “natural” course, relapse and prophylactic response in schizophrenic patients. Pharmacopsychiatry 16:206–211
Pocock SJ (1983) Clinical trials: a practical approach. Wiley. Chichester
Pogue-Seite MF (1989) The prognostic significance of negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry 155:123–127
Rutter DR, Draffan J, Davies J (1977) Thought disorder and the predictability of schizophrenic speech. Br J Psychiatry 131:67
Schooler NR, Kane JM (1986) Influences of pharmacologic and psychosocial factors on the course of schizophrenia. Psychopharmacol Bull 22:845–853
Schulze-Mönking H, Rook A, Stricker K, Buchkremer G (1986) Der Münsteraner Prognose Score—Ein prognostisches Instrument zur Einschätzung des Rehospitalisierungsrisikos ambulanter schizophrener Patienten. Psycho 12:395
Stevens BC (1973) Evaluations of rehabilitation for psychotic patients in the community. Acta Psychiatr Scand 49:169–180
Strauss JS, Carpenter WT (1974) The prediction of outcome in schizophrenia II. Relationship between predictor and outcome variables. Arch Gen Psychiatry 31:37–42
Strauss JS, Carpenter WT Jr (1977) Prediction of outcome in schizophrenia. III. Five-year outcome and its predictors. Arch Gen Psychiatry 34:159–163
Vaughn CE, Leff JP (1976a) The measurement of expressed emotion in the families of psychiatric patients. Br J Soc Clin Psychol 15:157–165
Vaughn CE, Leff JP (1976b) The influence of family and social factors on the course of psychiatric illness: a comparison of schizophrenic and depressed neurotic patients. Br J Psychiatry 129:125–137
WHO (1979) Schizophrenia: an international follow-up study. J Wiley, London
Wing JK (1982) Sozialpsychiatrie. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Zerssen D von, Koeller DM (1975) Die Paranoid-Depressivitäts-Skala. Beltz, Weinheim
Zubing J, Spring B (1977) Vulnerability—a new view of schizophrenia. J Abnorm Psychol 86:103–126
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was funded by the Ministry of Research and Technology of the Federal Republic of Germany
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buchkremer, G., Stricker, K., Holle, R. et al. The predictability of relapses in schizophrenic patients. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Nuerosci 240, 292–300 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02189543
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02189543