Summary
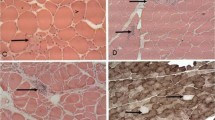
In the m. tibialis anterior of a 68-year-old man with rapidly developing denervation atrophy in the legs since 1/2 year prior to death from heart stroke, abundant unifocal concentric fiber changes, such as target, targetoid/core, and targetoid fibers could be observed. Besides, large vacuolized fibers with multiple changes resembling cytoplasmic bodies in the peripheral zone were present as well; they are interpreted as fibers with multicentric target or targetoid formations. The target fibers displayed a broad variation of their outer appearance suggesting a continuous transition to targetoid/core fibers (with a dense center) and targetoid fibers (with a central change to aquous sarcoplasm showing a paucity of fibrillar structures). Very few fibers with a central densification of fibrillar material with or without a thin intermediate zone were fairly akin to core fibers of central core disease; others were more alike the type of targetoid fibers, previously described in the literature, showing a dense target-like center; both were summarized under the term, inaugurated by Engel et al. (1966), “targetoid/core fibers”. Simultaneous occurence of the different kinds of concentric fiber changes suggested a strong relation between all of them in the sense of representing different developmental stages of the same pathogenetic process. Thus, the central core disease, for instance, might be a disorder with a generalization of concentric fiber changes having come to arrest in the earliest stage of development.
Zusammenfassung
Im M. tibialis anterior eines 68 Jahre alt gewordenen Mannes, der 1/2 Jahr vor seinem Tode am Herzinfarkt eine rasch progrediente neurogene Muskelatrophie in den Beinen entwickelte, fanden sich außerordentlich zahlreiche unifokal-konzentrische Muskelfaserveränderungen wie Target-, Targetoid/Core- und Targetoidfasern. Außerdem sah man große vacuolisierte Faserquerschnitte mit multiplen fokalen Veränderungen in der Randzone, die an die früher beschriebenen „cytoplasmic bodies“ erinnerten; im vorliegenden Zusammenhang wurden sie allerdings als Fasern mit multizentrischen Target- und Targetoidformationen interpretiert. Die Targetfasern zeigten eine weitläufige Variation in der äußeren Erscheinungsform, die in der Zusammenschau kontinuierliche Übergänge zu Targetoid/Corefasern (mit dichter Zentralzone) und Targetoidfasern (mit zentraler Auflösung und Vermehrung aquösen Sarkoplasmas mit wenigen fibrillären Strukturen) erkennen ließ. Wenige Fasern mit einer zentralen Verdichtung fibrillären Materials mit oder ohne schmaler Intermediärzone waren Corefasern des Central-Core-Disease auffallend ähnlich; andere glichen mehr dem Typ von Targetoidfasern mit strukturdichtem Zentrum, wie sie in der früheren Literatur beschrieben wurden. Beide Formen wurden wegen ihrer großen Ähnlichkeit von Engel et al. (1966) unter dem Begriff „Targetoid/Core Fibers“ zusammengefaßt. Das gleichzeitige Auftreten der verschiedenen Formen konzentrischer Faserveränderungen in einem Muskel legt die Annahme nahe, daß zwischen allen eine enge Beziehung im Sinne unterschiedlicher Manifestationsstufen des grundsätzlich gleichen pathogenetischen Prozesses besteht. So wäre unter dieser Annahme beispielsweise das Central-Core-Disease eine Erkrankung mit einer Generalisation konzentrischer Faserveränderungen, die im frühesten morphologischen Entwicklungsstadium zum Stillstand gekommen sind.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afifi, A. K., Smith, J. W., Zellweger, H.: Congenital nonprogressive myopathy. Central core disease and nemaline myopathy in one family. Neurology (Minneap.) 15, 371–381 (1965)
Aleu, F. P., Afifi, A. D.: Ultrastructure of muscle in myotonic dystrophy. Preliminary observations. Amer. J. Path. 45, 221–231 (1964)
Bethlem, J., Posthumus Meyjes, F. E.: Congenital non-progressive central core disease of Shy and Magee. Psychiat. Neurol. Neurochir. (Amst.) 63, 247–251 (1960)
Bethlem, J., van Gool, J., Hülsmann, W. C., Meijer, A. E. F. H.: Familial nonprogressive myopathy with muscle cramps after exercise. Brain 89, 569–588 (1966)
Dubowitz, V., Pearse, A. G. E.: Oxydative enzyme and phosphorylase in central core disease. Lancet 1960 II, 23–24
Dubowitz, V., Platts, M.: Central core disease of muscle with focal waisting. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat. 28, 432–437 (1965)
Engel, W. K.: Muscle target fibers, a newly recognized sign of denervation. Nature (Lond.) 191, 389–390 (1961)
Engel, W. K., Foster, J. B., Huges, B. P., Huxley, H. E., Mahler, R.: Central core disease—an investigation of a rare muscle cell abnormality. Brain 84, 167–185 (1961)
Engel, W. K.: The essentiality of histo- and cytochemical studies of skeletal muscle in the investigation of neuromuscular diseases. Neurology (Minneap.) 12, 778–794 (1962)
Engel, W. K.: The multiplicity of pathologic reactions of human skeletal muscle. Proc. 5th Intern. Congr. Neuropath., Zürich. Excerpta Med. Intern. Congr. Ser. 100, 613–624 (1965)
Engel, W. K., Brooke, M. H.: Histochemistry of the myotonic disorders. In: E. Kuhn, Progressive Muskeldystrophie, Myotonie, Myasthenie, pp. 203–222. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1966
Engel, W. K., Brooke, M. H., Nelson, P. G.: Histochemical studies of denervated or tenotomized cat muscle; illustrating difficulties in relating experimental animal conditions to human neuromuscular diseases. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 138, 160–185 (1966)
Gonatas, N. K., Perez, M. C., Shy, G. M., Evangelista, J.: Central “core” disease of skeletal muscle. Ultrastructural and cytochemical observations in two cases. Amer. J. Path. 47, 503–515 (1965)
Greenfield, J. G., Cornman, T., Shy, G. M.: The prognostic value of the muscle biopsy in the “floppy infant”. Brain 81, 461–484 (1958)
Martin, L., Reniers, J.: Etude histoenzymatique du muscle, 1. l'amiotrophie neurogene proximale (Kugelberg-Welander). Acta neuropath. (Berl.) 9, 328–334 (1967)
Resnick, J. S., Engel, W. K.: Target fibers—structural and cytochemical characteristics and their relationship to neurogenic muscle diseases and fiber types. In: Exploratory concepts in muscular dystrophy and related disorders (ed. A. T. Milhorat). Excerpta Med. Intern. Congr. Ser. 147, 255–267 (1967)
Schmitt, H. P.: Epi and intramedullary neurilemmoma of the spinal cord with denervation atrophy in the related skeletal muscles. Z. Neurol. (in press)
Schotland, D. L.: An electron microscopic study of target fibers, target-like fibers and related abnormalities in human muscle. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol. 28, 214–228 (1969)
Schröder, J. M., Adams, R. D.: The ultrastructural morphology of the muscle fiber in myotonic dystrophy. Acta neuropath. (Berl.) 10, 218–241 (1968)
Seitelberger, F., Wanko, T., Gavin, M. A.: The muscle fiber in central core disease. Histochemical and electron microscopic observations. Acta neuropath. (Berl.) 1, 223–237 (1961)
Shafiq, S. A., Milhorat, A. T., Gorycki, M. A.: Fine structure of human muscle in neurogenic atrophy. Neurology (Minneap.) 17, 934–948 (1967a)
Shafiq, S. A., Milhorat, A. T., Gorycki, M. A.: An electron microscopic study of muscle degeneration and changes in blood vessels in polymyositis. J. Path. Bact. 94, 139–147 (1967b)
Shy, G. M., Magee, K. R.: A new congenital non-progressive myopathy. Brain 79, 610–621 (1956)
Tomonaga, M., Sluga, E.: Zur Ultrastruktur der Targetfasern. Virchows Arch. Abt. A path. Anat. 348, 89–104 (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmitt, H.P., Volk, B. The relationship between target, targetoid, and targetoid/core fibers in severe neurogenic muscular atrophy. J. Neurol. 210, 167–181 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00316244
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00316244