Abstract
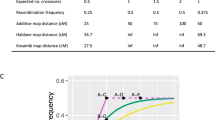
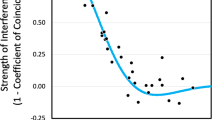
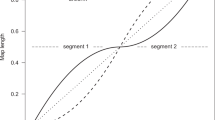
We have contructed a two–dimensional map of 243 markers on the X chromosome. The average distance between markers ordered by two recombinants is 5.4 centiMorgans(cM), which is reduced to 3.2 cM using a less stringent criterion of one recombinant. Map resolution is enhanced by replacing the usual reference marker format with a 2D format, and the two–recombinant rule is more conservative than the lod 3.0 criterion for order. Taken together, crossover mapping and the 2D format produces maps with greater reliability and higher resolution than maps constructed using currently accepted standards. This first high–density crossover–based map of an entire human chromosome provides a model for integrating physical and genetic maps.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Copeland, N.G. et al. A genetic linkage map of the mouse: current applications and future prospects. Science 262, 57–66 (1993).
Dietrich, W.F. et al. Agenetlc map of the mouse with 4,006 simple sequence length polymorphisms. Nature Genet. 7, 220–245 (1994).
Fain, P.R., Wright, E., Willard, H.F., Stephens, K. & Barker, D.F. The order of loci in the pericentric region of chromosome 17 based upon evidence from physical and genetic breakpoints. Am. J. hum. Genet. 44, 68–72 (1989).
Collins, F.S. & Galas, D. A new five-year plan for the U.S. Human Genome Project. Science 262, 43–46 (1993).
Ott, J. & Donis-Keller, H. Statistical methods in genetic mapping. Genomics 22, 496–497 (1994).
Wang, L.H., Collins, A., Lawrence, S., Keats, B.J.B. & Morton, N.E. Integration of gene maps: chromosome X. Genomics 22, 590–604 (1994).
Cox, D.R., Green, E.D., Lander, E.S., Cohen, D. & Myers, R.M. Assessing mapping progress in the Human Genome Project. Science 265, 2031–2032 (1994).
Keats, B.J.B. et al. Guidelines for human linkage maps: an international system for human linkage maps (ISLM,1990). Genomics 9, 557–560 (1991).
Thompson, E.A. Information gain In joint linkage analysis. IMAJ. Math. appl. Med. & Biol. 1, 31–49 (1984).
Matise, T.C., Pertin, M. & Chakravarti, A. Automated construction of genetic linkage maps using an expert system (MULTIMAP): a human genome linkage map. Nature Genet. 6, 384–390 (1994).
NIH/CEPH Collaborative Mapping Group. A comprehensive genetic linkage map of the human genome. Science 258, 67–86 (1992).
Buetow, K.H. et al. Integrated human genome-wide maps constructed using the CEPH reference panel. Nature Genet. 6, 391–393 (1994).
CHLC/UU/NIH.A comprehensive human linkage map with centlmorgan density. Science 265, 2049–2054 (1994).
Gyapay, G. et al. The 1993–94 Genethon human genetic linkage map. Nature Genet. 7, 246–339 (1994).
Green, P. Documentation for CRI-MAP, version 2.4 (1990).
Dietz-Band, J.N. et al. Isolation, characterization, and physical localization of 33 human X-chromosome RFLP markers. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 54, 137–141 (1990).
Barker, D.F. et al. High density genetic and physical mapping of DMA markers near the X-linked Alport Syndrome locus: Definition and use of flanking polymorphic markers. Hum. Genet. 88, 189–194 (1991).
Barker, D.F., Atkin, C.L., Gregory, M.C. & Fain, P.R. Applications of linked markers for genetic diagnosis of Alport Syndrome. InAdvances in Nephrology (ed. Tryggvason, K. ) (Karger, Basel, Switzerland, in the press).
Econs, M.J., Barker, D.F., Speer, M.C., Pericak-Vance, M.A. & Drezner, K. Multilocus mapping of the X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets gene. J. cllin. endocrinol. Metab. 75, 201–206 (1992).
Econs, M.J. et al. Flanking markers define the X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets gene locus. J. Bone Min. Res. 8, 1149–1152 (1993).
Econs, M.J. et al. Fine structure mapping of the human X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets gene locus. J. 0in. endocrinol. Metab. 79, 1351–1354 (1994).
Fain, P.R., Barker, D.F. & Chance, P.F. Refined genetic mapping of X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy. Am. J. hum. Genet. 54, 229–235 (1994).
Fain, P.R. et al. Localization of the highly polymorphic microsatellite DXS456 on the genetic linkage map of the human X chromosome. Genomics 11, 1155–1157 (1991).
Lafreniere, R.G. et al. Physical mapping of 60 DNA markers in the p21.1-q21. 3 region of the X chromosome. Genomics 11, 352–363 (1991).
Barker, D.F. & Fain, P.R. Definition and mapping of STSs at STR and RFLP loci in Xp11–Xq22. Genomics 18, 712–718.
Willard, H.F. et al. Report of the Fifth International Workshop on human X chromosome mapping 1994. Cytogenet. Cell Genet., 67, 295–358 (1994).
Ott, J. Analysis of Human Genetic Linkage (Baltimore, Johns Hopkins University Press, 1991).
Liu, L. et al. Automated construction of highly accurate meiotic mapping panels for human chromosome 7 using BINS. Am. J. hum. Genet. 55, A194 (1994).
Litt, M. et al. The CEPH consortium linkage map of human chromosome 11. Genomics (in the press).
Mandel, J.L. Genome maps III. Science 258, 87–102 (1992).
Schlessinger, D., Mandel, J.L., Monaco, A.P., Nelson, D.L. & Willard, H.F. Report and abstracts of the Fourth International Workshop on human X chromosome mapping 1993. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 64, 147–194 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fain, P., Kort, E., Chance, P. et al. A 2D crossover–based map of the human X chromosome as a model for map integration. Nat Genet 9, 261–266 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0395-261
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0395-261