Abstract
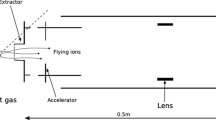
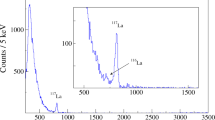
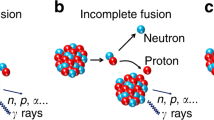
WE have measured the cross-section of the deuteron for disintegration by γ-rays of effective energy 6.13 and 17.6 MeV. The results are:  (both these uncertainties are probable errors). The γ-rays were obtained, in the first case, by bombarding thick targets of calcium fluoride with protons of energy 890 keV., and, in the second, by bombarding thick targets of lithium hydroxide with protons of energy 500 keV. The disintegrations were produced in an ionization chamber of volume 475 c.c. containing deuterium at a pressure of 38 atmospheres; the pulses from the resulting protons were analysed by a ninety-nine channel kick sorter. An identical chamber, filled with ordinary hydrogen, was used for estimating the various background effects. The γ-ray flux from the fluorine target was measured by counting the α-particles emitted prior to the de-excitation of the residual oxygen-16 nucleus. The flux of higher energy γ-rays was measured with a thick-walled graphite ionization chamber: confidence in the computations was increased by the agreement (within 3 per cent) between the values of the 6.13-MeV. γ-ray flux deduced by this method, and by the more certain α-particle counting method. In the reduction of the results, allowance has been made for the small and known inhomogeneity of the γ-rays in both cases. The energies of the γ-rays have been adopted from the work of Walker and McDaniel1, and their relative intensities from this work and from that of Burcham and Freeman2. For the purpose of these slight corrections, the form of the dependence of cross-section on γ-ray energy given by the “old” theory3 has been assumed.
(both these uncertainties are probable errors). The γ-rays were obtained, in the first case, by bombarding thick targets of calcium fluoride with protons of energy 890 keV., and, in the second, by bombarding thick targets of lithium hydroxide with protons of energy 500 keV. The disintegrations were produced in an ionization chamber of volume 475 c.c. containing deuterium at a pressure of 38 atmospheres; the pulses from the resulting protons were analysed by a ninety-nine channel kick sorter. An identical chamber, filled with ordinary hydrogen, was used for estimating the various background effects. The γ-ray flux from the fluorine target was measured by counting the α-particles emitted prior to the de-excitation of the residual oxygen-16 nucleus. The flux of higher energy γ-rays was measured with a thick-walled graphite ionization chamber: confidence in the computations was increased by the agreement (within 3 per cent) between the values of the 6.13-MeV. γ-ray flux deduced by this method, and by the more certain α-particle counting method. In the reduction of the results, allowance has been made for the small and known inhomogeneity of the γ-rays in both cases. The energies of the γ-rays have been adopted from the work of Walker and McDaniel1, and their relative intensities from this work and from that of Burcham and Freeman2. For the purpose of these slight corrections, the form of the dependence of cross-section on γ-ray energy given by the “old” theory3 has been assumed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walker, R. L., and McDaniel, B. D., Phys. Rev., 74, 315 (1948).
Burcham, W. E., and Freeman, R., Phys. Rev., 75, 1756 (1949)
Bethe, H., and Peierls, R., Proc. Roy. Soc., A, 148, 146 (1935).
van Allen, J., and Smith, N., Phys. Rev., 59, 618 (1941).
Wäffler, H., and Younis, S., Helv. Phys. Acta, 22, 414 (1949).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BARNES, C., STAFFORD, G. & WILKINSON, D. Photo-electric Disintegration of the Deuteron at 6.13 and 17.6 MeV.. Nature 165, 69–70 (1950). https://doi.org/10.1038/165069b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/165069b0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.