Abstract
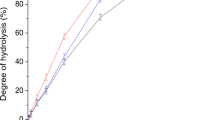
IN a recent paper, Hopkins, Jelinek and Harrison1 have studied the hydrolysis of potato amylose to maltose with the enzyme, beta amylase. These workers found that the hydrolysis proceeds at a continually diminishing rate and that it is never a first-order reaction as has been claimed by some workers2,3. From a study of the products at various stages of the hydrolysis, the theory advanced to explain the facts is that the longer chains of amylose are hydrolysed at a faster rate than short chains and that the longer chains are attacked first. This would account for a continually diminishing rate of hydrolysis as the reaction proceeds and as the length of the chains gradually becomes shorter. From data presented in a recent paper4, and from other considerations which were briefly mentioned at that time, we have presented a rather different view to explain similar observations.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hopkins, R. H., Jelinek, B., and Harrison, L. E., Biochem. J., 43, 32 (1948).
Meyer, K. H., and Bernfeld, P., C.R. Soc. phys. et hist. Nat., 22 (1940).
Meyer, K. H., “Natural and Synthetic High Polymers", 4, 415 (Interscience Publishers, Inc., New York, 1942).
Cleveland, F. C., and Kerr, R. W., Cereal Chem., 25, 133 (1948).
Kerr, R. W., and Severson, G. M., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 65, 193 (1943).
Cleveland, F. C., and Kerr, R. W., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 71, 16 (1949).
Swanson, M., J. Biol. Chem., 172, 805 (1948).
Swanson, M., and Cori, C. F., J. Biol. Chem., 172, 815 (1948).
Swanson, M., J. Biol. Chem., 172, 825 (1948).
Meyer, K. H., Noelting, G., and Bernfeld, P., Experientia, 3, 370 (1947).
Bernfeld, P., and Gürtler, P., Helv. Chim. Acta, 31, 105 (1948).
Meyer, K. H., Bernfeld, P., Gürtler, P., and Noelting, G., Helv. Chim. Acta, 31, 108 (1948). See also, J. Phys. Coll. Chem., 53, 319 (1949).
Kerr, R. W., Paper Trade J., 115, No. 22, 30 (1942).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KERR, R. Action of Beta Amylase on Amylose. Nature 164, 757–759 (1949). https://doi.org/10.1038/164757b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/164757b0
This article is cited by
-
Mechanism of the Beta-Amylolysis of Amylose
Nature (1950)
-
Action of Î-Amylase on Amylose
Nature (1949)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.