Abstract
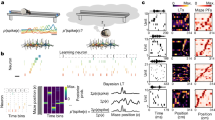
In associative learning, the activated neurones undergo a variety of concomitant functional alterations—increases or decreases of firing activity1–4 and modifications of membrane potential or resistance5–8 and of synaptic responsiveness9–11 . Synaptic transmission which can be strengthened only when there is paired activity in two pathways is of particular interest in relation to mechanisms for associative learning12,13. For the neocortex, there are few observations of the plastic changes, induced by conditioning procedures, in the effectiveness of individual synapses14–17. We now report that various regimes with joint stimulations of convergent excitatory pathways on to intracellularly recorded neurones in the motor cortex of the cat result in synaptic facilitation lasting for up to 30 min.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kandel, E. R. & Spencer, W. A. Physiol Rev. 48, 65–134 (1968).
Berger, T. W. & Thompson, R. F. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 1572–1576 (1978).
Morrel, F. in The Neurosciences, A Study Program (eds Quarton, G. C., Melnechuk, T. & Schmitt, F. O. ) 452–469 (Rockefeller University Press, New York, 1967).
Morrel, L. T., Hoeppner, T. J. & Morrel, F. Science 204, 528–530 (1979).
Alkon, D. L. Science 205, 810–816 (1979).
Woody, C. D. & Black-Cleworth, P. J. Neurophysiol. 36, 1104–1115 (1973).
Kandel, E. R. & Tauc, L. J. Physiol., Lond. 183, 287–304 (1966).
Hoyle, G. Neurosci. Res. Prog. Bull. 17, No. 4, 577–586 (1979).
Kandel, E. R. & Tauc, L. J. Physiol., Lond. 181, 1–47 (1965).
Kandel, E. R. & Tauc, L. Nature 202, 145–147 (1964).
Voronin, L. L. in Soviet Research Reports Vol. 2 (ed. Woody, C. D. ) (Brain Information Service, University of California, Los Angeles, 1976).
McNaughton, B. L., Douglas, R. M. & Goddard, G. V. Brain Res. 157, 277–293 (1978).
Gardner-Medwin, A. R. Trans. Biochem. Soc. 6, 841–844 (1978).
Voronin, L. L. Acta neurobiol. exp. 40, 1B, 335–370 (1980).
Baranyi, A. & Fehér, O. Expl Brain Res. 33, 283–298 (1978).
Baranyi, A. & Fehér, O. Expl Brain Res. 41, 124–134 (1981).
Tzebelikos, E. & Woody, C. D. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 4, 81 (1978).
Nelson, P. G. & Frank, K. J. Neurophysiol. 30, 1097–1113 (1967).
Kandel, E. R. in The Neurosciences, A Study Program (eds Quarton, G. C., Melnechuk, T. & Schmitt, F. O. ) 666–689 (Rockefeller University Press, New York, 1967).
Hebb, D. O. The Organization of Behaviour (Wiley, New York, 1949).
Konorski, J. Conditioned Reflex and Neurone Organization (Cambridge University Press, London, 1948).
Heinemann, U. & Lux, H. D. Brain Res. 93, 63–76 (1975).
Koike, H., Mano, N., Okada, Y. & Oshima, T. Expl Brain Res. 14, (1972).
Moody, W., Futamachi, K. & Prince, D. A. Expl Neurol. 42, 248–263 (1974).
Misgeld, U., Sarvey, J. M. & Klee, M. R. Expl Brain Res. 37, 217–229 (1979).
Lynch, G., Gall, C. & Dunwiddie, T. Prog. Brain Res. 48, 113–130 (1978).
Bindman, L. J., Lippold, O. C. J. & Milne, A. R. J. Physiol., Lond. 286, 457–477 (1979).
Woody, C. D., Swartz, B. E. & Gruen, E. Brain Res. 158, 373–375 (1978).
Takahashi, E. J. Neurophysiol. 27, 908–924 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baranyi, A., Fehér, O. Synaptic facilitation requires paired activation of convergent pathways in the neocortex. Nature 290, 413–415 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1038/290413a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/290413a0
This article is cited by
-
Habituation and sensitization in primary headaches
The Journal of Headache and Pain (2013)
-
Long-term motor cortex plasticity induced by an electronic neural implant
Nature (2006)
-
Synchronization and cooperative interaction in brain activity
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology (1995)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.